03/09/2021

M12 Connectors, Their Coding, and Applications
When you need an M12 connector for a project, one question always follows:
What type of M12 connector do you need?
The range of M12 connectors we distribute is extensive. To help you choose the right one, we’ve summarized the different codes and their applications below.
Distinctions
At first glance, distinguishing one M12 connector from another can be challenging. The main differences lie inside the connector. The way the connector is locked and how the pins are configured—to prevent mismatching or enable secure connections—makes each connector unique. These configurations are determined by the connector’s “coding.” Codings are essential for identifying and differentiating between various connectors.
Because field technicians need to quickly disconnect, reconnect, and install connectors, codings also ensure that an M12 connector is never plugged into the wrong circuit or used in an incorrect application. If you attempt to insert an M12 connector into the wrong socket, it simply won’t fit.
Applications
A wide range of coding options make M12 connectors suitable for various applications. You’ll commonly find M12 connectors in agriculture, alternative energy, communications, factory automation, instrumentation, robotics, and transportation.
Codings
Below is a quick overview of what the most common M12 codings mean and where they can be used. The five most common M12 connector codings are as follows:
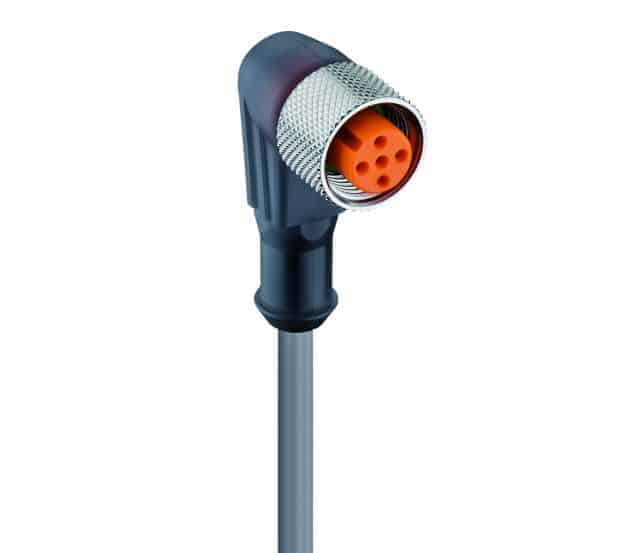

- M12 A-coded connectors are widely used and have been around for decades. They’re also the most versatile in terms of the types of connections they support and the number of pins in the connector (anywhere from three to 12 or even more). They support DC connections and are used to connect sensors and actuators as well as Ethernet connections up to Category 5e (four-pair connections).
- M12 B-coded connectors are for network or non-Ethernet fieldbus connections (most commonly PROFIBUS) and can also be used for sensor connections. Over time, these connectors may see less use as PROFIBUS and similar fieldbus protocols are replaced by Ethernet.
- M12 C-coded connectors are used for AC applications, including motor connections. We anticipate that some applications currently requiring M12 C-coded connectors may eventually shift to K- and S-coded connectors (see below for more details).
- M12 D-coded connectors are primarily used for industrial Ethernet connections, such as PROFINET and EtherNet/IP. They support a form factor for two-pair connections. Unlike M12 X-coded connectors, D-coded connectors do not support Gigabit Ethernet; they only support Fast Ethernet (100 Mb/s).
- M12 X-coded connectors are a more recent development specifically designed to support Gigabit Ethernet. These connectors prevent mismatching and feature walls between each pair of pins (totaling four pairs of two pins). The walls prevent crosstalk and interference, achieving high-performance standards for Category 6 or 6A (up to 10 Gb/s).
Additional Codings
Additional M12 codings are available for power connections that support higher voltage and current levels than standard M12 connections. The pins in these connectors are spaced to ensure proper electrical characteristics and prevent incorrect connections:
- M12 K- coded connectors have five pins, are designed for AC connections (AC motors, motorized switches, PSUs, etc.), and are rated for 630 volts.
- M12 S-coded connectors have four pins, are also designed for AC connections, and are rated for 630 volts.
- M12 L-coded connectors have four or five pins, are designed for DC connections (DC motors and drives, LED fixtures, I/O modules, etc.), and are rated for 63 volts.
- M12 T-coded connectors have four pins plus a functional grounding pin, are also designed for DC connections, and are rated for 63 volts.
- Lastly, the M12 Y-coded connector is a hybrid connector that supports both power and data connections through the same connector; an internal wall separates the power and data pins. This can save valuable space and reduce installation time and materials in applications that require both.
Do you still have questions about the different codings after reading this article or need a quote? Feel free to contact one of our advisors. We’re here to help!